A Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) is a cluster of specific geographic areas that governments choose to develop large-scale renewable energy projects. The area has abundant renewable energy resources (like wind, solar or hydro), good land conditions, existing infrastructures, and strong commercial interest for new generation projects.
In Australia, EnergyCo’s REZ program in NSW has become pioneers in shifting toward a future powered mostly by clean energy fed into Australia’s National Electricity Market (NEM). Malaysia and parts of Latin America are also moving in a similar direction as they plan more coordinated renewable energy development.
REZs in NSW, Australia’s leading REZ pioneer
The NSW Government is establishing REZs across the state to replace ageing coal-fired power stations with a more reliable, low-cost, and cleaner energy supply.
The five selected REZs — Central-West Orana, South West, Hunter-Central Coast, Illawarra and New England — have excellent sun and wind resources and good access to existing power lines. These REZs power energy to homes and businesses through high-voltage power lines that can support long-term industries.
Central‑West Orana
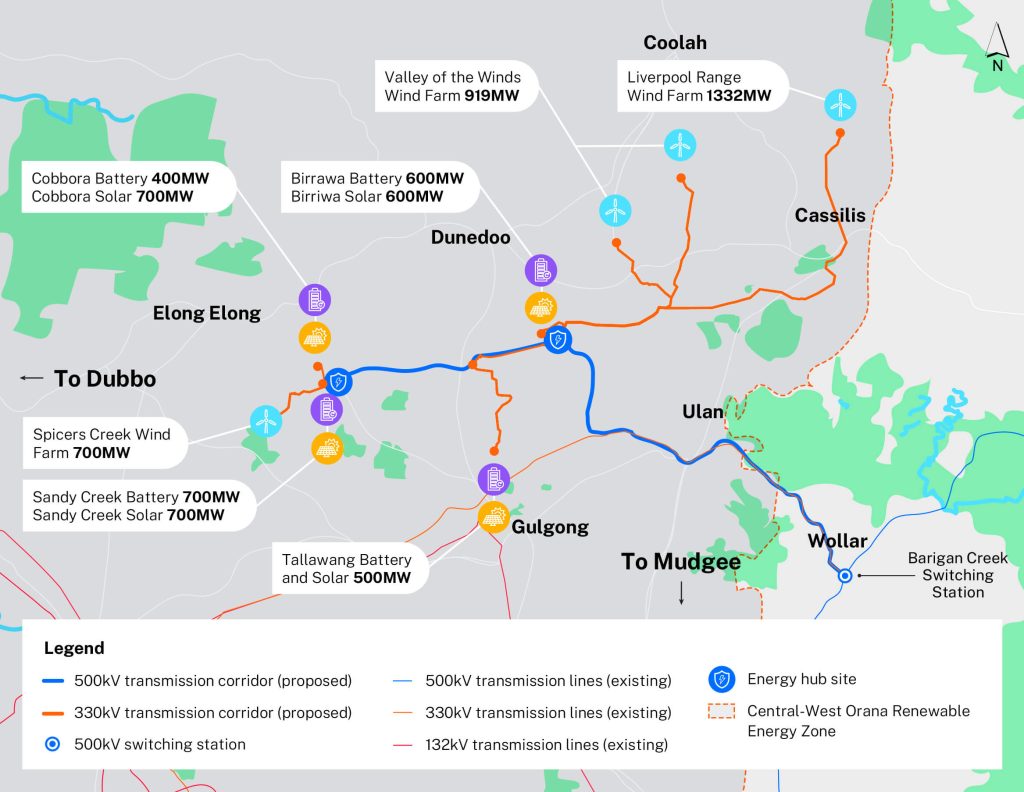
Source: Central West Orana REZ projects map
NSW is now delivering its first REZ in the Central-West Orana region that covers around 20,000km2 near Dubbo and Dunedoo region, on Wiradjuri, Wailwan and Kamilaroi Country.
It is designed to unlock at least 4.5GW of new electricity capacity by the late-2020s.The transmission lines will allow power from solar and wind projects to flow into the wider grid.
The projects include:
- transmission project that have received NSW planning approval in June 2024 to connect the Central-West Orana REZ to the existing grid and in mission to operate and maintain it for the next 35 years
- generation and storage projects that will connect to electricity with the combination of renewable energy generation projects and battery energy storage.
Beyond meeting electricity demand, REZs are expected to deliver strong economic benefits to local manufacturing, transport, retail and service industries. The zones are forecast to attract up to $25 billion in private investment, support around 1,850 local jobs each year during construction, and create about 930 ongoing roles from 2034.
Arche Energy has been supporting the development of the Central West Orana REZ since 2022 where our Principal Consultant, Matthew Richards, is the Candidate Foundational Generators (CFG) Coordinator. He’s managing engagement between EnergyCo and renewable energy developers.
New England REZ
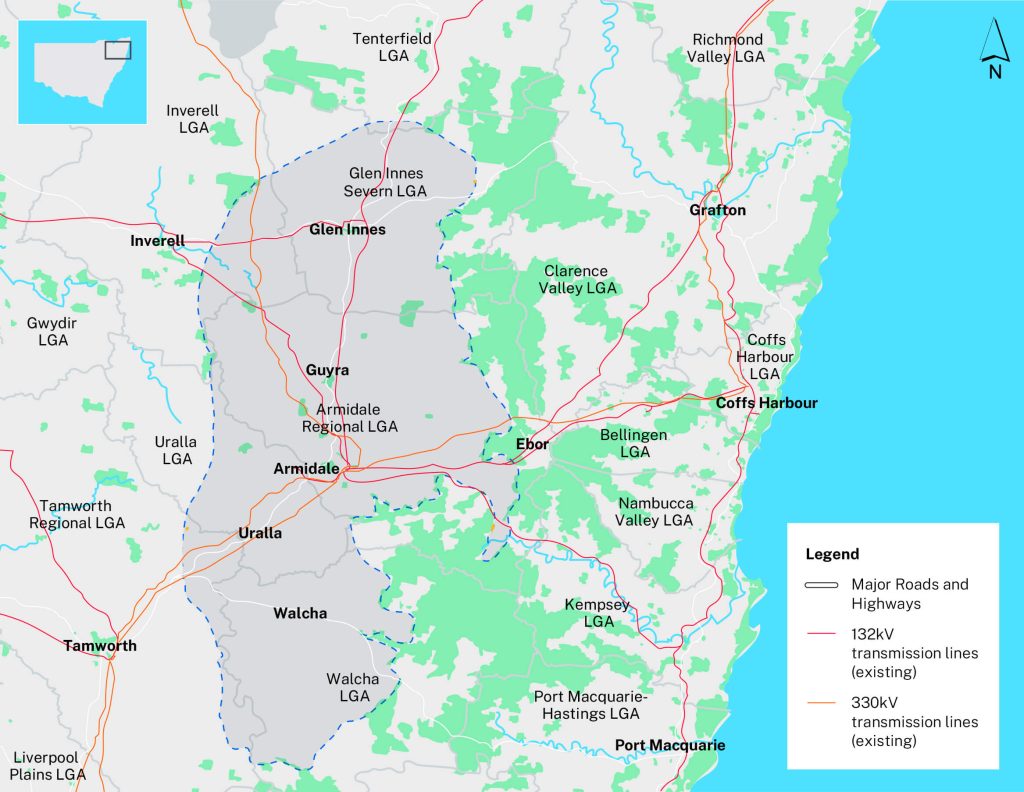
Source: New England REZ
The New England REZ was officially declared by the Minister for Energy under section 19(1) of the Electricity Infrastructure Investment Act 2020 (the Act), with the decision formally published in the NSW Gazette on 17 December 2021. By the time, the government received 80 registrations of interest, adding up to 34GW of potential renewable projects.
Now it is progressing in the early planning centred around Armidale. The zone is planned to support around 8GW of clean energy, with expectations to bring in up to $24 billion in private investment.
The region has capacious wind, solar, and pumped-hydro potential in the country, and is also close to existing power lines to make it easier to plug new projects into the grid. At the same time, it opens the door to send extra energy to Queensland when there’s surplus in the south.
Arche Energy is also playing a role in the New England REZ. Our Principal Consultant, David Nolan, supported the Candidate Foundation Generator selection process and coordinates closely with generators. He acted as the key link between the transmission project and major renewable energy developers.
Another of our Principal Consultants, George Mellick, is currently Commercial Manager — Performance Regime, which means he is responsible for the development of the Network Operator’s Performance Regime contract documentation and metrics. The regime incentivises and applies a penalty to the network operators regular service payments based on the network operator’s performance against contractual and legislative requirements such as network reliability.
South West REZ
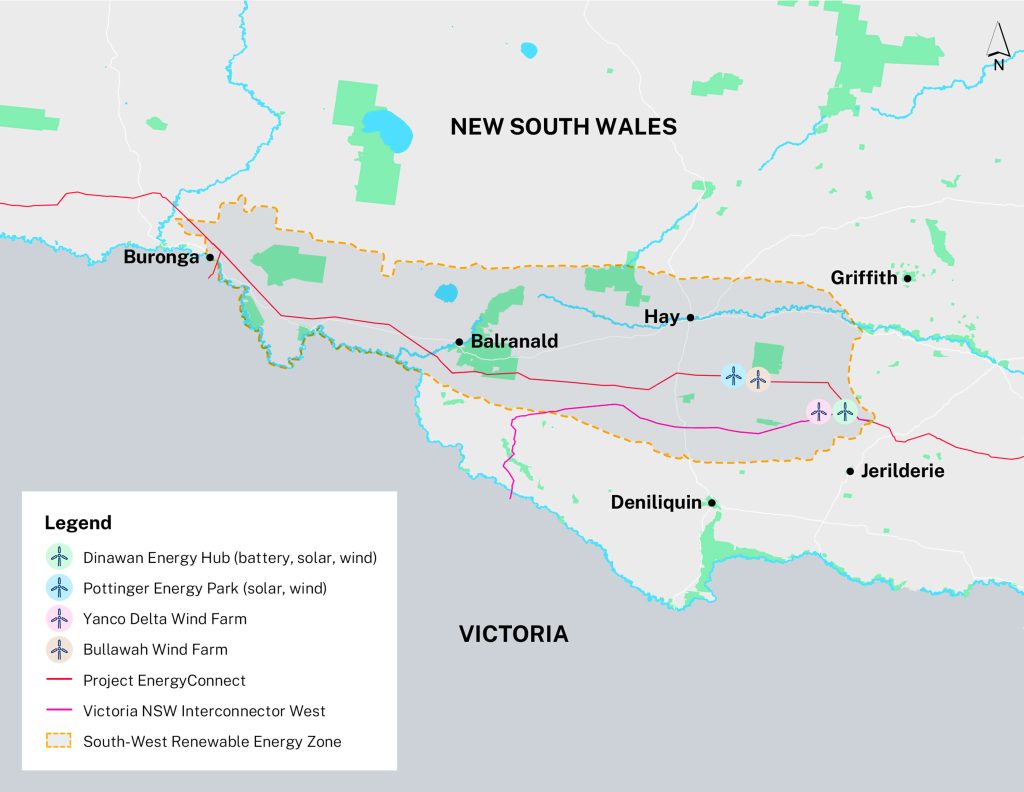
Source: South West REZ
The South West REZ will deliver 3.56GW of clean energy over the next decade. The zone runs from Dinawan Substation in the east to Buronga Substation in the west.
The area was chosen as it has:
- strong wind and solar resources
- close to existing and planned high-voltage transmission lines
- good land-use compatibility
- and a solid pipeline of proposed renewable projects.
The REZ includes:
- 2 major transmission projects: Project EnergyConnect and Victoria to NSW Interconnector West (VNI West)
- 4 renewable energy projects: wind, solar, and battery storage infrastructure.
On the economic side, it’s expected to deliver cheaper electricity to up to 1.6 million homes and businesses. Attract more than US$17.8 billion in private investment and create around 1,690 local jobs each year during construction.
Hunter-Central Coast REZ
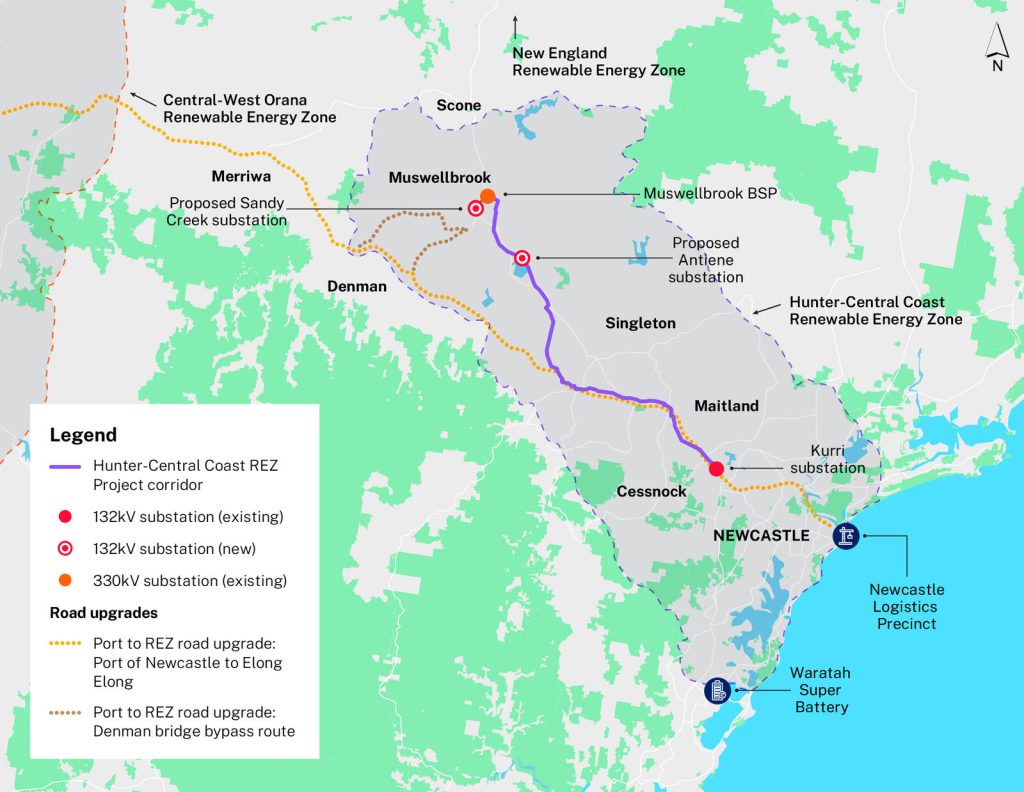
Source: Hunter-Central Coast REZ
The Hunter-Central Coast has abundant wind and solar sources. The area stretches from the lands of Awabakal, Bahtabah, Biraban, Darkinjung, Mindaribba, Wanaruah and Worimi.
Initially, the REZ is planned to support around 1GW of network capacity, but the capacity can grow over time as coal-fired power stations retire, mining land is repurposed, and offshore wind is developed. This does not include the Hunter Transmission Project, which could unlock up to 8GW of extra capacity from inland REZs, to help cut emissions from major industries like Tomago Aluminium.
During the registration of interest process, proposals poured in representing almost 40GW of renewable generation and storage and more than $100 billion in potential investment. They interested in:
- 24 solar energy projects
- 13 onshore and 7 offshore wind energy projects
- 35 large-scale batteries
- 8 pumped hydro projects.
The Hunter-Central Coast REZ will play a big role in Australia’s renewable future to support renewables like green hydrogen, ammonia and metals production, offshore wind, electric vehicle fleets and cleaner industrial processes.
Illawarra REZ
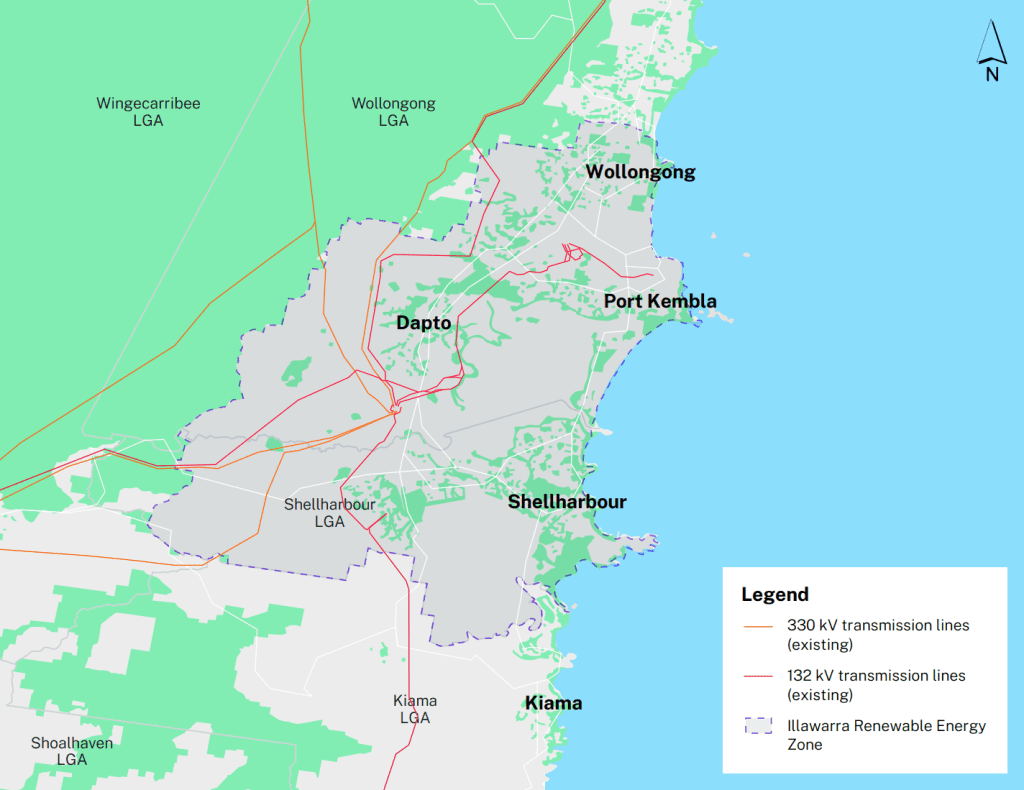
Source: Illawarra REZ
The NSW’s first urban REZ will deliver 1GW network capacity. This capacity is predicted to increase along with the growth of the green hydrogen industry and green steel manufacturing. The project will also support new low-carbon industries to expand opportunities for green manufacturing as demand grows both locally and globally.
Located around Wollongong to Dapto and the Shellharbour LGA, this entire area was chosen because it has:
- major energy resources
- existing port and transport infrastructure
- skilled workforce ready
- future renewable energy projects potential.
The Illawarra REZ will deliver comprehensive energy resources, such as rooftop solar, home batteries, and community-scale batteries. As the project lead, EnergyCo will use existing government land and commercial rooftops to minimise impacts on local communities and the surrounding environments.
REZ development across the rest of Australia
NSW has led the charge for REZ development since 2020, followed by Victoria and Queensland to build their long-term cluster new generation transmission plans with REZs. In practice, REZs are strategically becoming the backbone of Australia’s renewable energy rollout as the country works toward its 82% renewables target by 2030.
Victoria
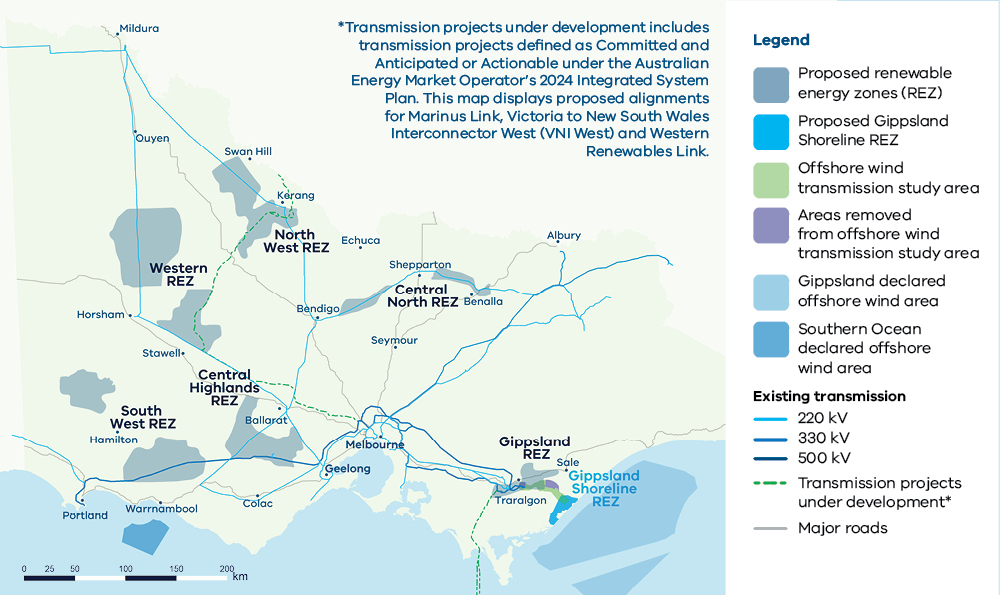
Source: Victoria REZ
REZ is Victoria’s new approach to deploying renewable energy for the community and Traditional Owners benefits, while minimising the bad impact on industries and the environment. It also aimed to reduce pressure on the transmission network, and map clearer paths to developing renewable energy projects.
The proposed REZ, as stated in The 2025 Victorian Transmission Plan, pinpoints 6 potential zones:
- South West
- Central Highlands
- Western
- North West
- Central North
- Gippsland (covers shoreline areas where underground cables will connect power from offshore wind farms onto the grid).
The planned zones were chosen based on factors, including:
- strong wind and sunshine resources
- nearby transmission lines
- whether renewable projects could sit alongside farming
- the potential impacts on the environment, the local communities, and culturally significant areas for Traditional Owners.
Note: Not all requests from the community or industry have been adopted in the final zone locations.
For its progress, the Minister has released draft renewable energy zone orders. Each draft orders take up:
- the zone map
- transmission projects to enable the zone
- the planned storage capacity that can be supported by the planned transmission network in the zone.
The government is also calling for another round of feedback before each zone is officially declared.
Queensland
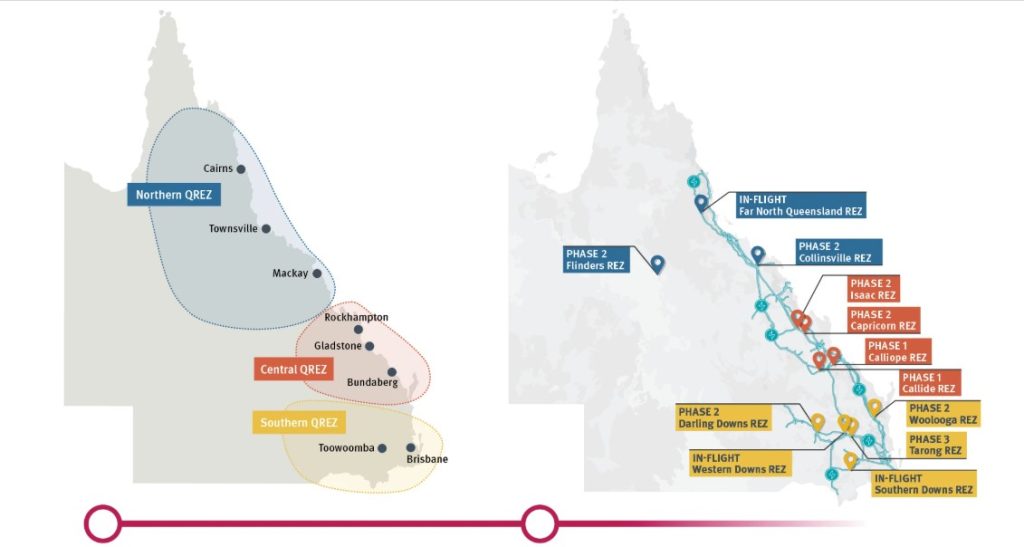
Source: Queensland REZ
In 2024, the Queensland Government released the Queensland Renewable Energy Zone Roadmap which identified 12 potential zones based on network capacity, project pipeline, and land use analysis. These zones include:
Southern Queensland REZs:
- Southern Downs REZ (in-flight)
- Western Downs REZ (in-flight)
- Woolooga REZ (planning)
- Darling Downs REZ (planning)
- Tarong REZ (planning).
Central Queensland REZs:
- Callide REZ (planning)
- Calliope REZ (planning)
- Isaac REZ (planning)
- Capricorn REZ (planning).
North and Far North Queensland REZs:
- Far North Queensland REZ (in-flight)
- Collinsville REZ (planning)
- Flinders REZ (planning).
The zone’s development requires the following four stages:
Stage 1: Planning the REZ
Working with local communities and the renewable energy sector to understand whether an area is suitable for a REZ.
Stage 2: Consultation and Declaration
Running formal consultations on a draft REZ Management Plan to give communities a real chance to shape how the REZ will be built and developed.
Stage 3: Construction and Operation
Building and running the REZ, including new or upgraded network infrastructure and energy projects.
Stage 4: Commissioned
The REZ becomes fully operational, with all projects connected, running, and operating for at least the next 15 years.
Overall, the Roadmap outlines how approximately 22GW of new solar and wind power will be deployed across the zones, to drive Queensland achieve its renewable energy targets.
The Queensland Government expects efficiency savings that could cut down household electricity bills, while also creating a strong jobs pipeline of around 4,000 direct construction roles in the renewable energy industry.
Malaysia: Emerging REZ-like structures in its energy transition
Malaysia’s National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) launched in July 2023 outlines the nation’s focus to expand the economy and deliver new energy sector business opportunities. And, the planned 1GW integrated REZ is one of the major opportunities highlighted for the renewable energy project.
The Ministry of Economy Malaysia has introduced a Renewable Energy Zone (RE Zone) project, which covers:
Integrated RE Zone
A large-scale integrated sustainable development led by Khazanah Nasional will encompass the entire energy supply chain, from power generation and storage to smart energy use.
The RE Zone pilot will covers:
- industrial park
- zero-carbon city
- residential areas
- data centre.
Solar park
Large Scale Solar (LSS) PV Park 4 is a major solar project delivering 100MW per site across five locations in several states. The project is co-developed by TNB, working with SMEs, cooperatives and state economic development corporations.
According to GlobalData, which tracks more than 170,000 power plants worldwide, the project is currently at the announced stage. The development will be in a single phase.
Hybrid hydro-floating solar PV (HHFS)
A plan to unlock up to 2,500MW HHFS at existing TNB hydro dam reservoirs. Key project highlights:
- lower cost by using existing hydro infrastructure
- scale up for green hydrogen production in future
- uses hydro reservoirs as natural energy storage by conserving water in reservoirs during peak hours and releasing it during off-peak hours
- availability of 24-hour renewable energy.
The development will be in 4 phases. A milestone to Malaysia’s shift from a traditional fossil fuels-based economy to a high-value green economy with installed renewable energy capacity target set to 70% by 2050.
As Malaysia builds out these early clean‑energy zones, working with consultants who have hands-on experience in NSW REZ projects, like Arche Energy, can guide the country to develop a coordinated renewable energy planning and operations strategy.
Latin America: Chile
In April 2025, the Ministry of Energy of Chile released the Long-Term Strategic Planning (PELP) 2023-27 that sets out an official policy instrument to assure Chile’s power sector remains sustainable and resilient.
For the first time in the energy sector, the ministry also announced Polos de Desarrollo de Generación Eléctrica (PDGE), also known as Electricity Generation Development Hubs, the maps for long-term energy planning to 2050 targets.
This contains a draft of five new renewable energy development zones in more than 112,000 hectares, stretching from Antofagasta (96,682 hectares) and Tocopilla (15,758 hectares).
The zones are planned to deliver 19,945MW of potential clean energy capacity to position the regions as major hubs in Latin America for future clean energy growth. Overall, it’s a big step forward for Chile’s clean energy transition.
Arche’s experience in supporting REZ‑style development globally
With experience built through work on NSW REZ‑related projects, Arche Energy brings a practical understanding of how REZ development functions in real‑world settings.
This perspective supports governments, stakeholders, and developers in places with emerging markets like Malaysia and Chile as they are in the early stage forming their own renewable clusters.
Arche is just a click away to help you draw on proven approaches while adapting to local conditions and policy. To start a conversation to clean energy transition, click Enquiry Now.
